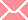Music that is associated with divine grace and form becomes celestial. A Flute is one such instrument which holds divine values. According to the Hindu mythology, the Flute was the link between Lord Krishna and his beloved consort Radha. Today, it is an essential and integral part of classical Indian music. Though simple in appearance, the sound of the humble Flute manages to hypnotise the listener. The mesmerizing and velvet tones of the simple Flute create an unbroken trance. Since times immemorial, the Flute has existed in different cultures of the world. The Indian name for the Flute is Bansuri and Venu. It belongs to the wood wind family of musical instruments. They are also classified as edge–blown aero phone type. The modern music ensembles of orchestras and symphonies also include the Flute. Let us learn more about this instrument in detail.
Ancient Flute was considered as an instrument of the common people. According to Hindu religious scriptures, Flute was the companion of Lord Shri Krishna. Historical evidences points out to the finding of a Flute–like musical instrument to a period as early as the Stone Age. It is considered the first ever wood wind instrument. The Chinese and the Egyptians were the first to innovate the finger–holes on the bamboo Flute. The 1st and the 4th centuries saw the existence of the transverse Flute in Europe and Rome. Later, during the 16th–18th century period, various changes were made to the standard bamboo Flute which was made out of wood. Boehm, an 18th century flautist made innovative changes in the body of the Flute which gained wide acceptance and set the standards for modern day Flutes. It was during the 19th and 20th centuries that the Flute was able to attain international standard with a modified body and a number of tone holes and powerful notes. The bamboo Flute is still used by common people whereas the modified versions are used in modern ensembles and solo renditions.

A Flute works on the mechanism of blowing air through the mouth hole. When the flautist blows through the mouth hole (embouchure hole), the stream of air which is in contact with the edges is directed in and out in a cyclical motion. This cyclical motion or vibrations are responsible for sound generation. The vibrations excite the air column inside the cylindrical body of the Flute. The tone holes and keys are effectively used by the flautist to shorten the vibration, thus, producing an increased pitch. The open lower end and the open keys are responsible for sound projection. The expert key work is primarily responsible for sound production of a Flute rather than blowing of air.

The important parts of a Flute include the crown, embouchure(mouth hole),lip plate, tubing or body made up of head joint, middle joint and foot joint, barrel and key or finger–holes.
The early Flutes were simple, single piece, handmade and were mostly made from wood, reeds and bamboos. Modern Flutes are made of different components, including those from wood or metal. The manufacturing process includes shaping, assembling, forming, mounting and finishing. Each part is shaped according to an individual Flute. The process of shaping is done through die casting. The keys may be connected in an individual cast or a single strip and is trimmed into shape. The assembling involves the immersing of keys in a chemical solution to enable soldering. All the different connecting parts are soldered together. The keys are then cleaned. They are then fitted to pads made of cork with felt covering. The tone holes where the keys will fit in are formed in the body of the Flute. The tone holes are drilled with precision. Once the tone holes are made, supporting rods are soldered to the body of the Flute. Keys are mounted to these rods with screws and pins. Surface tension to hold the pads is provided by springs. All the other parts such as the mouth piece and the joints are fitted tightly and the Flute is tested for performance.

A Flute is counted amongst the oldest wood wind instruments of the world. It is an essential part of traditions, rituals and beliefs. In India, the Flute is regarded as a divine gift from the most revered deity, Lord Shri Krishna. The tradition of playing the Flute is more of a spiritual experience. It is an important part of North Indian classical music as well as Carnatic music of the South. Flute has been played in orchestras, symphonies, sonata, jazz, rock and solo rendition as well as accompaniments. It is an important feature of the instrumental music.

Flutes are classified into different types, depending upon the various cultures and beliefs. They include:
- Panpipes: Originating from the Greek culture, this type of Flute is made of 5 pipes. It is a folklore instrument related to the Greek God Pan.
- The Ocarina: It is a very simple instrument which can play all the notes and is widely used in Japan.
- The Recorder: This is the oldest musical instrument of the wood wind family but is still in use. It resembles the modern day Flute.
- Sulina: It is a Flute having six holes and is found in Bali, Indonesia. Sulina is a type of Flute made from bamboo and is also known as the humming instrument.
- Shakuhachi: It is made of bamboo and belongs to the Japanese traditional genre. From playing solo to pop music and movie tracks, the Japanese think the sound of Shakuhachi leads to the path of enlightenment.
- Bansuri: Made from bamboo, the Indian Flute is widely used in classical music. The Bansuri is looked upon more as a means of spiritual enhancement because of its association with the revered Hindu deity, Lord Krishna.
- Dizi: A six–fingered Flute made from bamboo, Dizi has its origin in China. It is believed to be about 9000 years old but is still popular in China and is played horizontally.
- Fife: Although it is a small instrument, it is played in marching bands and drills. The sheer pitch of the Fife can be heard miles away.
- Irish Tin whistle: A traditional instrument of the Celtic folk music, it resembles the fipple Flute of Germany.
Modern Flutes: Types of modern Flutes are Bass Flute, Tenor Flute, Alto Flute, Concert Flute, Soprano Flute, Treble and Piccolo.

Legendary composers such as Mozart, Beethoven, Antonio Vivaldi, Bach and Joseph Haydn have played Flute in their operas, orchestral works, chamber music, musical arrangements and solo works. Late. Pannalal Ghosh and Pandit Hariprasad Chaurasia are notable Bansuri exponents from India. Ian Anderson of Jethro Tull, Tim Weisberg (jazz, rock fusion) and Chris Wood are the modern day Flute players.

Established Flute players can be sought for guidance. Some beginners may learn to play in weeks, months, a year or more than a year to become an expert flautist. However, there are music schools in UK, USA, Germany, India and other countries that teach Flute. Indira Kala Sangeet University and Akhil Bhartiya Gandharva Mahavidyalaya in India teach Flute. The learning process involves:
- Buying/ renting a Flute and assembling its parts (if a modern Flute).
- Start with holding the Flute properly with the left hand on the upper keyholes and the right hand on the lowest part of the Flute.
- Learn by ‘tonguing’ on it and not by blowing. Practice to place the right fingers on the right keys.
Follow the notes and charts for reference.