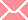We all know that there is a region in the sky called Water. This region is home to many water–related constellations such as Pisces, Eridanus and Aquarius. However, there is one constellation which lies in the Water region of the sky but is not considered one of the Zodiac constellations. It is Cetus. Cetus is a constellation that passes very close to the border of zodiac constellations and accordingly some of the planets and asteroids can be occasionally be seen in it. Catalogued by Ptolemy in the 2nd century, it belongs to the Perseus family of constellations. The name of this constellation was derived from a mythological character named Cetus. It was a sea monster sent to kill a princess. Cetus is also at times, referred to as the Whale. It is best visible in the month of November at 9 pm.
Cetus contains nine stars with known planets. Some of them are:
- Deneb Kaitos (Diphda) or Beta Ceti: It is the brightest star in this constellation. Its name is derived from the Arabic phrase Al Dhanab al Ḳaiṭos al Janūbīyy meaning ‘the southern tail of Cetus’. It is an orange giant and has left the main sequence stage of evolution on its way of becoming a red giant. The star is slightly cooler than the sun as its surface temperature is about 4,800 k (4,526° C). With an apparent magnitude of about 2.04, it is approximately 96.3 light years distant from the earth.
- Menkar (Menkab) or a Ceti: It is an old red–giant star. The name Menkar comes from the Arabic word for ‘nostril’. Eventually, the star ejects its outer layers to form a planetary nebula, thereby leaving a large white dwarf remnant. It has an apparent visual magnitude of about 2.54 and is approximately 249 light years distant.
- Mira–o Ceti (Omnicron Ceti): It is a binary star. It consists of a red giant and a companion star. The word Mira means ‘wonderful’ in Latin. About 6,000 and 7,000 known stars belong to this group, out of which, those whose surfaces oscillate to cause variations in brightness ranging from 80 to more than 1,000 days are all red giants. It was the first non–supernova star discovered and is believed to be about six billion years old. It lies about 420 light years away from the earth.
- τ Ceti or tau Ceti: It is a cool class G dwarf and one of the nearest star to the earth and the solar system. With a mass of about 78% of that of the sun, Tau Ceti’s luminosity is equal to only 55% of its luminosity. A metal–deficient star with high proportion, it is one of the very few stars that are nevertheless, visible to the naked eye. Its apparent magnitude is about 3.5 and is approximately 11.9 light years distant.
- UV Ceti: It is a binary star consisting of two red dwarfs.
It does have a couple of deep sky objects. Some of the notable ones include:
- Messier 77 (M77, NGC 1068): It is a barred spiral galaxy. One of the largest galaxies listed in Messier’s catalogue, it is approximately 47 million light years away from the earth. Its apparent visual magnitude is about 9.6.
- NGC 1055: It is a spiral galaxy that lies next to M77. It is seen edge–on and is a known radio source. It is approximately 52 million light years distant.
- NGC 1087: It is an intermediate spiral galaxy. There are a lot of irregular features in the disk of material surrounding it. It is a small central bar and its nucleus is extremely small. The galaxy is approximately 80 million light years distant.
- NGC 1073: This is another galaxy in Cetus which is believed to have an H II nucleus and has an apparent magnitude of about 11.5.
- NGC 45: A barred spiral galaxy discovered by the English astronomer John Herschel in 1835, it has a magnitude of about 10.4 and is 32.6 million light years away from the earth.
- NGC 17: It is a spiral galaxy which is believed to have formed as a result of the merger of two disk galaxies. With an apparent magnitude of about 15.3, it lies about 250 million light years distant from the earth.
- NGC 47 or NGC 58: It is a barred spiral galaxy that appears like a spiral nebula with a bright core. It was discovered by the German astronomer Ernst Wilhelm Lewis Swift Tempel and was also known as NGC 58. It has an apparent magnitude of about 13.5 and is approximately 236 million light years distant from the earth.
- NGC 1042: A spiral galaxy located near NGC 1035, NGC 1042 is believed to be physically associated with each other due to their similar red shifts.
Seen at latitudes between +70 and -90, it lies in the first quadrant of the southern hemisphere.
It occupies an area of 1,231 square degrees, making it the 4th largest constellation in the night sky. The closest star in this constellation is UV Ceti which is 15 light years distant from the earth while the furthest star is 420 light years distant. Hence, it can be said that Cetus is 420 light years distant from the earth.
Cetus is a sea monster from the mythological story associated with Andromeda and Cepheus constellations. It was commonly depicted as a hybrid creature with forefeet, huge jaws and a scaly body like a giant sea serpent.
Cetus is surrounded by constellations such as Aquarius, Aries, Eridanus, Fornax, Pisces, Sculptor and Taurus.